Artificial Active Immunity Graph
The first line of defence in a human body against pathogens is through barriers such as the skin mucus layers and saliva. The protection against infectious disease conferred either by the immune response generated by immunization or previous infection or by other nonimmunologic factors.

The Adaptive Immune Response B Lymphocytes And Antibodies Anatomy And Physiology Ii
Active immunity This is when the body is activated and produces the antibodies needed to fight an infection.

. This is again produced by innate immunity. Define the method by which a host distinguishes itself from nonself foreign materials 2. Artificial induction of immunity makes individuals resistant to explicit infections by implies other than sitting tight for them to come down with the sickness.
Artificially acquired active immunity is protection produced by intentional exposure of a person to antigens in a vaccine so as to produce an active and lasting immune response. The IFT appears to be a more sensitive. As human or animal blood plasma or serum as pooled human immunoglobulin for intravenous ivig or intramuscular ig use as high-titer human ivig or ig from immunized donors or from donors.
3 Immunity in which non-self antigens trigger an anti-self immune reaction after a period of sensitisation. Define artificial active immunity. The second line of defence is through phagocytes.
As human or animal blood plasma as pooled human immunoglobulin for intravenous or intramuscular IG use and in the form of monoclonal antibodies MAbPassive transfer is used prophylactically in the case of. Diagram the host cell receptors that distinguish self from nonself 3. Established on a microbe hypothesis of irresistible.
Active immunity can be acquired through natural immunity or vaccine-induced immunity. This type of immunity is further divided into artificial and natural immune systems. It encompasses the capacity to distinguish foreign material from self and to neutralize eliminate or metabolize that.
Artificially acquired passive immunity preformed antibodies or lymphocytes produced by one host are introduced into another host 11 12 344 Recognition of Foreignness 1. The third line of defence is through adaptive immunity. The immune system to develop its own defences against the disease.
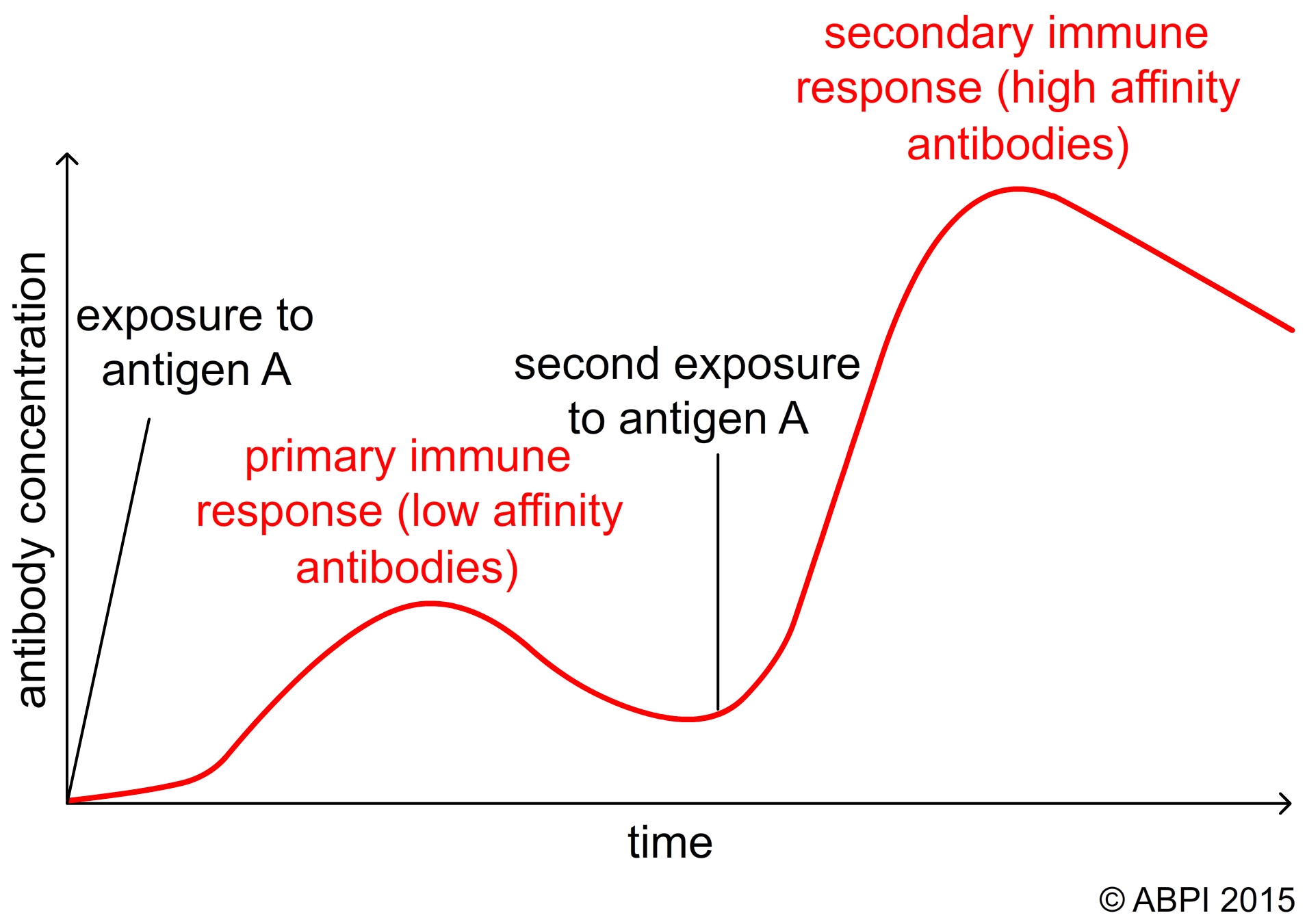
The antigens in the vaccine stimulate the immune system to produce antibodies and memory cells which are specifically directed against the antigens in the vaccine. Artificially acquired passive immunity is a short-term immunization induced by the transfer of antibodies which can be administered in several forms. Artificial Vaccination can artificially stimulate active immunity.
The magnitude of the lymphocyte transformation reaction was higher in the naturally infected than in the vaccinated group P less than 001. ĭ-munĭ-te the condition of being immune. This is known as artificial active immunity whereas the kind of immunity that develops when the immune system comes into contact with the infectious agents of disease often making you ill is known as natural active immunity.
Active Immunity Active Immunity results when exposure to a disease organism triggers the immune system to produce antibodies to that disease. It takes a little longer to do its job since it involves the use of a wide range of cell types. The white blood cells in your immune system come across the proteins from the viruses bacteria and other foreign elements.
Active immunity is defined as immunity to a pathogen that occurs following exposure to all or part of that pathogen. Immunity obtained either from the development of antibodies in response to exposure to an antigen as from vaccination or an. Immunity against diseases that can cause serious illness is valuable.
Thus antibody responses to VZV were better in naturally infected than in vaccinated subjects. Artificial active immunity synonyms artificial active immunity pronunciation artificial active immunity translation English dictionary definition of artificial active immunity. One vaccinated subject had VZV-specific IgA and IgM in the serum.
When the body is exposed to a novel disease agent a cascade of signaling molecules and action from the innate immune system results in activation of the adaptive immune system. Natural immunity is acquired from exposure to the disease organism through infection with the actual disease. 2 Any compromise in immune function unrelated to inherited defects in the immune system.
Active Immunity Process. It is your bodys highly complex immune system that locates identifies and destroys pathogens and toxins. 1 Any immune response to exogenous antigens.
This is known as innate immunity. Your immune system learns about these proteins present in those bacteria and virus cells and creates a protein surface to surround the antigen. Artificially acquired passive immunity is a short-term immunization achieved by the transfer of antibodies which can be administered in several forms.
In brief this is where the body is exposed to a dead or weakened form of the pathogen which though unable to mount an infection still activates the adaptive immune response and. The design is to diminish the danger of death and suffering.

Defense Against Disease Active And Passive Immunity Plantlet
Comments
Post a Comment